Under The Light Microscopic View
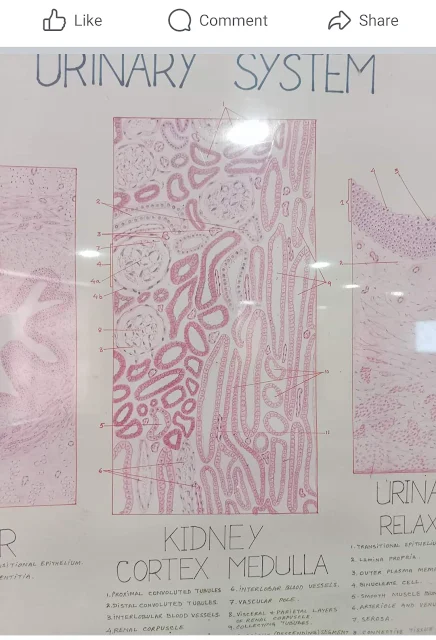
Identifying the cortex and medulla of the kidney on histology slides involves recognizing specific features unique to each region. Here are key identification points for kidney cortex and medulla histology:
Kidney Cortex:
Renal Corpuscles (Glomeruli):
- The cortex contains renal corpuscles, which consist of glomeruli (networks of capillaries) surrounded by Bowman's capsules.
- Glomeruli are responsible for the initial filtration of blood to form urine.
Proximal and Distal Convoluted Tubules:
- Tubules originating from Bowman's capsules include the proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) and the distal convoluted tubules (DCT).
- PCT is closer to the renal corpuscle, while DCT is farther away.
Cortical Collecting Ducts:
- The collecting ducts, where the processed filtrate is further modified, are present in the cortex.
- These ducts transport the urine towards the medullary region.
Cortical Labyrinths:
- The arrangement of renal corpuscles, proximal and distal tubules, and collecting ducts creates a labyrinthine appearance in the cortex.
Renal Columns (Cortical Columns):
- Extensions of cortical tissue called renal columns extend into the medulla, providing support and containing blood vessels.
Kidney Medulla:
Renal Pyramids:
- The medulla consists of triangular structures called renal pyramids.
- Each pyramid has a base facing the cortex and a papilla (nipple-like structure) pointing towards the renal pelvis.
Renal Papilla:
- The renal papilla is the tip of the renal pyramid where urine drains into the minor calyx.
Loop of Henle:
- The loops of Henle, part of the nephrons, extend into the medulla from the cortex.
- They play a crucial role in concentrating urine.
Medullary Rays:
- Striped structures called medullary rays extend from the renal cortex into the medulla.
- These rays contain collecting ducts and blood vessels.
Interlobar Arteries and Veins:
- Interlobar arteries and veins run within the renal columns, transporting blood between the cortex and medulla.
Cortical-Medullary Junction:
- The boundary between the cortex and medulla is known as the cortical-medullary junction.
Connective Tissue:
- Connective tissue surrounds and supports the structures in both the cortex and medulla.
Staining Characteristics:
- Stains like hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) can be used to differentiate cellular structures and enhance visibility.
written by : Ikrambiagtech.blogspot.com
Facebook page Focus click below 👇 image
Telegram channel
Download free video





















0 Comments